
The Power of Online Reviews on Purchase Decisions
Today, buying a product often starts with reading online reviews. Star ratings and detailed testimonials influence consumer behavior. These snippets of feedback impact our decisions due to the psychological principles that guide human decision-making. The research article “Examining the Effect of Positive Online Reviews on Consumers’ Decision-Making: The Valence Framework” by Lin Xiao and Yuan Li explores the relationship between online reviews and consumer behavior.
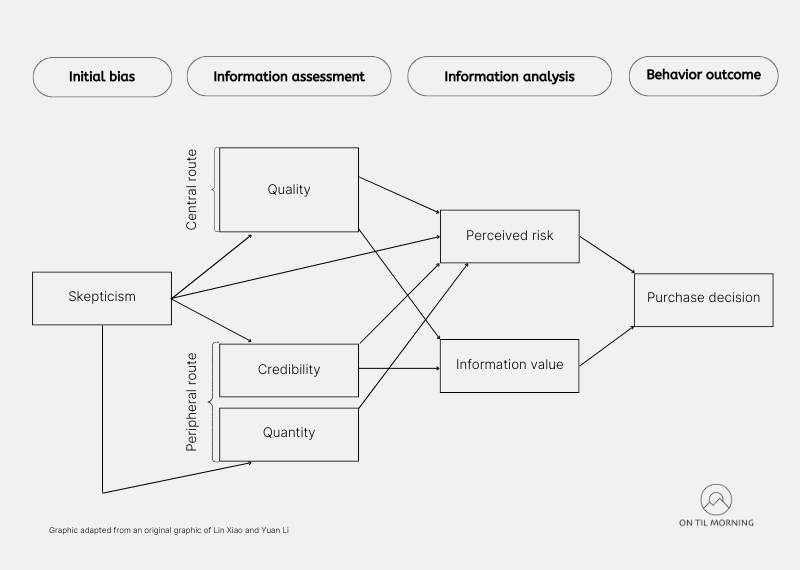
The study combines two well-known theoretical models: the Elaboration Likelihood Model and the Valence Framework.
Elaboration Likelihood Model Developed by Petty and Cacioppo (1986), proposes people process information through either a central or a peripheral route. The central route requires significant cognitive effort as individuals assess the quality of the argument’s content. Conversely, the peripheral route depends on the credibility of the source and the quantity of reviews.
Valence Framework Proposed by Peter and Tarpey (1975), the Valence Framework examines how consumers balance perceived risks and benefits to maximize positive outcomes and minimize negative consequences.
By combining these models, the researchers show how online reviews affect consumer behavior through cognitive evaluation and mental shortcuts. The study looks at how positive reviews impact perceived usefulness and risk, influence behavior, and the role of skepticism.
Key Findings
- The study found that perceived usefulness positively influences consumer behavior, while perceived risk has a significant negative effect. These findings are consistent with the valence framework’s premise that both benefits and risks play important roles in decision-making. Once consumers form an impression of a product, they tend to seek information that confirms that belief. Reviews provide a substantial amount of validation.
- One of the most powerful psychological drivers behind the influence of online reviews is social proof. When faced with uncertainty, people tend to look to others to determine how to act. The quality of arguments and the credibility of sources were found to hold significant value to consumers. High-quality, persuasive arguments and credible sources increased the value of the information. However, the quantity of reviews did not affect information value, indicating that content quality and credibility are more important than the number of reviews.
- The study found that skeptical consumers saw higher risks despite quality reviews from credible sources, while less skeptical consumers were more influenced by positive reviews. For those with low skepticism, strong arguments, credible sources, and many reviews reduced perceived risk. However, for highly skeptical consumers, these factors had no effect or even increased perceived risk due to doubts about review authenticity.
Implications for Marketers and Businesses
Understanding the psychological principles behind online reviews can help businesses craft more effective marketing strategies. By encouraging authentic feedback, addressing negative reviews, and leveraging social proof, brands can build trust and influence consumer purchase decisions.
- Focus on Argument Quality and Source Credibility: Businesses should generate high-quality, informative, and persuasive content. Using credible sources for reviews may enhance consumer trust.
- Managing Review Volume: Although the number of reviews can indicate product popularity, businesses should not rely only on this metric. Quality and credibility are more influential in shaping consumer perceptions.
- Addressing Consumer Skepticism: People tend to trust opinions from experts or experienced individuals. Online reviews often include credentials like “Verified Buyer” tags or top reviewer statuses to enhance credibility. Platforms should implement measures to verify review authenticity and highlight reliable contributors. Increasing transparency about the origins of reviews can help reduce consumer skepticism.
- Tailored Communication Strategies: Understanding the skepticism levels of target audiences can inform communication strategies. For highly skeptical consumers, businesses should emphasize authenticity and transparency. Engage with negative feedback to demonstrate a commitment to customer satisfaction.
Limitations
- Sample Generalizability: Conducted on a single Chinese platform, limiting broader applicability.
- Focus on Positive Reviews: Only positive reviews were studied, ignoring negative ones.
- Self-Reported Data: Possible biases from self-reported data.
Future Research Directions
The research by Lin Xiao and Yuan Li underscores the significant role that online reviews play in shaping consumer behavior. By integrating the Elaboration Likelihood Model and the Valence Framework, the study offers a comprehensive understanding of how cognitive evaluation and mental shortcuts influence purchase decisions. Key findings highlight the importance of perceived usefulness, argument quality, and source credibility in reducing perceived risks, while skepticism can either amplify or mitigate the impact of reviews.
For businesses and marketers, the practical implications are clear: fostering authentic and credible reviews, addressing skepticism, and focusing on quality content are critical strategies for building consumer trust and driving purchasing decisions. Platforms that verify review authenticity and showcase credible sources can better mitigate consumer doubts and enhance engagement.
However, the study’s limitations highlight the need for further research. Future investigations should explore the impact of negative reviews, conduct cross-platform analyses, and examine cultural variations in review perception to provide a more holistic understanding.
In an era where digital feedback reigns, brands that prioritize authenticity, transparency, and value-driven content will be best positioned to thrive. Consumers will always seek validation—and businesses that provide it through trustworthy reviews will gain a competitive edge.
